Stratasys 3D Printing: Different 3D Printing Technologies

While Stratasys has always been the pioneer of 3D printing, it’s important to know that there are many different types of technologies and materials surrounding 3D printing, also known as “additive manufacturing”.
Stratasys 3D printers use one of two technologies. The ever popular “Fused Deposition Modeling”, FDM, and the “Polyjet” technology.
FDM

FDM is the main 3D printing technology that everyone knows about and has seen. Real engineering grade thermoplastics are made into a filament, round up in a spool, and then fed from the spool to a heat extrusion tip and laid down layer by layer. Like a hot glue gun affixed to a CNC milling machine, except adding material each layer and not taking away.
This technology has been imitated by hundreds of different companies and people because it is the most cost effective and easy to use.
Polyjet
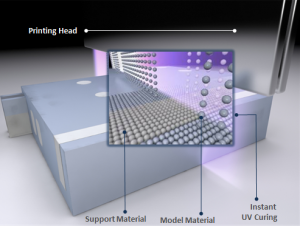
Polyjet works more like a normal ink printer, but uses a UV curable resin instead of ink. The head passes over the tray, distributes tiny precise droplets of resin, and a UV light comes over and cures the resin. This process is repeated on top of the layer before until the part is done. Polyjet parts are acrylic based thermoset plastics and thus are used in different applications then thermoplastics like with FDM.
Some of the other 3D printing technologies not represented with Stratasys machines include:
Stereolithagraphy
Stereolithagraphy, Stereolithography, uses a UV curable photopolymer, like Polyjet. The difference is that the polymer usually sits in an open tank or vat and is selectively cured. UV lasers or projected light is concentrated onto a build tray, and a thin film of the polymer is cured in the desired geometry. This process is then repeated on top of the last layer until completion.
Selective Laser Sintering
Selective Laser Sintering, SLS, is a process that can be used with a variety of materials from plastics to metals. The concept is nearly same as Stereolithography, but instead of a liquid polymer and light, it uses powdered materials and heat. A build platform is covered with a thin film of the powder, then a laser sinters, or fuses, the powder in the desired area. a new film or layer of powder gets spread across the last and the process is repeasted.
Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting utilizes the sweeping process, like Polyjet and normal ink printing, while also using a powdered material like with SLS. A binder, or glue, is dispersed on to a thin layer of powder in the desired areas, and then a new layer of powder material is added on top and steps repeated. After being jetted, the binder will solidify the powder in place. Using Binder Jetting, parts can be made basically out of material that can be made into a powder and react with some sort of liquid binder.
There are many other additive manufacturing processes and technologies and new ones being created all the time. Hybrids of old and new technology, like 3D printing with cement using an extrusion process like FDM, or completely new ones. 3D printing isn’t a fad. It’s adaptive and growing, and I don’t see it going away any time soon.
Cody Doiron
Computer Aided Technology

 Blog
Blog