Thermal Resistance definition for thermal contact
In thermal analysis of assemblies, SOLIDWORKS Simulation lets you define thermal contact resistance values. This allows you to model the thermal effect of a layer of a material which is too thin to mesh in 3D. However, the user needs to input the value of the resistance. Here is a primer on how to calculate the thermal resistance:
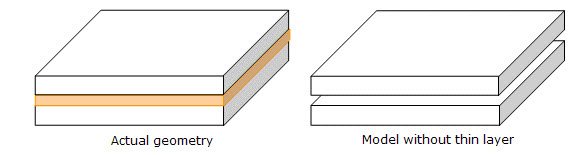
The expected value is either the total or distributed resistance, respectively in K/W or (K.m²)/W in the SI unit system.
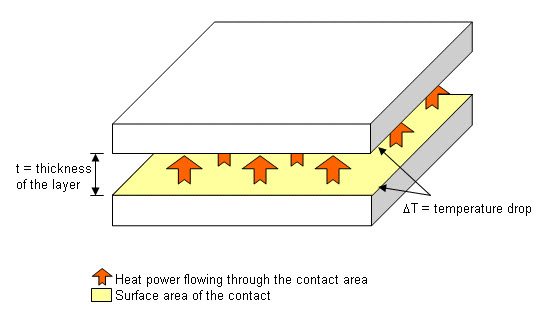
The basic formula for temperature drop in a thin layer of material between two parts is given by:
DT = q * [t / (k * A)]
where:
DT= temperature drop at the contact zone in K
q = heat power flowing through the contact in W
t = thickness of the layer in m
k = thermal conductivity of the layer material in W/(mK)
A = surface area of the contact in m²
The total thermal resistance is t/(k*A) and the distributed resistance is t/k.
Thermal conductivity required to have a given thermal resistance
You can also determine the thermal conductivity required to have a given thermal resistance.
For a material of constant thickness, the total thermal resistance is Rt = t/(k*A) and the distributed resistance is Rd = t/k.
With:
t = thickness of the layer in m
k = thermal conductivity of the layer material in W/(mK)
A = surface area of the contact in m²
Therefore, you can calculate the required thermal conductivity k to use in a material of thickness t to have the thermal resistance you need: k = t/(Rt*A) or k = t/Rd.

 Blog
Blog